GCSE Grading System: What Do the Numbers Mean?
Employers who review apprentice CVs regularly will know that the GCSE grading system changed a few years back. However, it can be very confusing trying to review an apprentice CV without a clear understanding of the grading system. Here we will explain the new(ish) system and what the numbers mean.
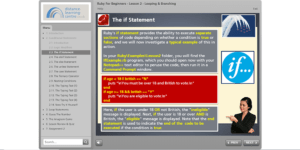
In 2017, the GCSE grading system changed in the United Kingdom. The new GCSE grading system moved away from letter grades altogether. Instead, students are given a number grade from 0-9.

The new scale recognises more clearly the achievements of high-attaining students, as the additional grades allow for greater differentiation. Changing from letters to numbers also allows anyone – for example an employer – to see easily whether a student has taken a new, more challenging GCSE, or an old reformed GCSE.
So what do the numbers mean? The highest grade that a student can get is a nine. This is equivalent to an A*. The next highest grades are 8 and 7, which are equivalent to an A. Grade 6 is equivalent to a B. Grades 5 and 4 are both C equivalents, with 5 classed as a strong pass and 4 as a standard pass.
We hope this article has helped to clear up any confusion about the GCSE grading system. Employers must be aware of the numbered system, so they can understand grading on CVs when reviewing candidates. If you have any questions or need help recruiting an apprentice, please do not hesitate to get in touch with us.