Digital Support Technician Apprenticeship
The broad purpose of someone on a Digital Support Technician Apprenticeship is to maximise the effective use of digital office technologies, productivity software and digital communications. These will include collaborative technologies, and digital information systems.
A Digital Service Technician (DST) supports external customers and clients through a wide variety of digital channels. A DST helps them access and receive services and provides coaching and support to them in their use of the digital systems. A DST will support external customers and clients to complete and submit data remotely. They will help them to diagnose and resolve problems with their access to and use of digital tools.
In their daily work, Digital Support Technicians interact with a wide variety of internal or external users of digital systems. They will communicate through digital channels, by phone and/or face to face. Digital Support Technicians work under general direction, using discretion in identifying and dealing with complex issues. They receive clear instructions and have their work reviewed at frequent milestones and determine when issues should be escalated to a higher level. Digital Support Technicians interact with and influence others, having working level contact with colleagues or customers. They may supervise others or make decisions which impact the work assigned to others or to other phases of projects. A Digital Support Technician plans, schedules and monitors their own work within limited deadlines and according to relevant law, standards and procedures.
Digital Service Technicians (DST) help customers and clients register for and access data, products and services through online and digital channels. This can be as part of a sales or customer service process. They support and coach external users in their use of these digital systems. They diagnose and resolve external users’ digital problems with accessing and using digital tools. A DST also advises on related hardware and software problems. They use software packages and tools such as collaborative technologies, to interface effectively with external end-users. They will use a variety of digital channels to maximise effective external user support and to resolve external end-user problems. A DST will use and maintain information systems such as Customer Relationship Management tools to manage service delivery, improve user experience and increase efficiency.
Knowledge
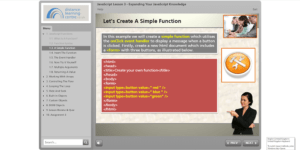
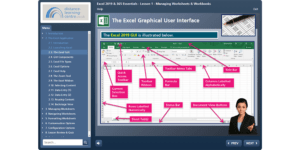
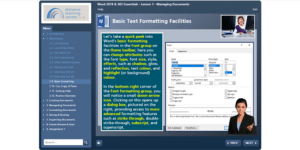
- digital office automation technologies; • how to use them to create, update, edit, manage, and present data• the organisation’s use of templates and their best working practice• how these tools can be used to collaborate with others
- types of digital architecture and how it relates to their organisation;• physical storage versus cloud• role of operating systems and servers
- the importance of backing up data securely and the technologies that support it.
- the principles, processes and procedures for the secure handling of data in compliance with legislation.
- the concepts and fundamentals of data;· searching, storing, integrating, and organising data· how organisations use various types of data· the key features and functions of information systems· data formats and their importance for analysis· data entry and maintenance
- the key principles and processes for diagnosing stakeholder’s digital problems.
- principles of a helpdesk system, including accessing and maintaining stakeholder information and the contribution of helpdesk system to the organisations performance and customer service.
- approaches to risk mitigation for data loss including confidentiality, integrity and availability
- significance of an organisation’s digital presence;· how this is maintained and what products are used· how the brand is represented and safeguarded
- approaches to a range of communication channels and how to adapt to different audiences and situations.
- the principles and constraints of searching the internet and accessing information securely • Currency- Relevance- Authority- Accuracy- Purpose
- approaches to planning and organising own learning activities to maintain and develop digital skills (CPD).
- approaches to effective time management and prioritisation
- principles of continuous improvement within the context of the application and use of digital technologies and the benefits
- current and emerging digital technologies and the possible implications for work on a support desk including the impacts of digital technologies for climate change, sustainability and moving to net carbon zero
- approaches to assessing the impact of their actions on other stakeholders within a support desk environment
- the components of databases and their use
- approaches to stakeholder system configurations and how this impacts on providing technical support
- the importance and security implications of updating and maintaining stakeholders systems.
- approaches to minimising and communicating the impact of required technical procedures.
- approaches to the training and support of stakeholders to make the best use of the organisation’s digital systems.
Skills
- use digital technologies, including collaborative tools, to operate effectively as part of a team, and with other stakeholders, enabling sharing of information and best practice.
- use data accurately and securely to meet business requirements and in line with organisational procedures and legislation.
- apply information security principles, for example: information transfer, deletion, storage, usage and communications that may include using mobile devices.
- provide an appropriate and effective response to enquiries, providing support and information utilising digital channels and in line with organisation protocols
- operate digital information systems, for example• Management- Finance Human Resources• Bespoke departmental or organisational systems or databases
- communicate effectively through a variety of different channels using terminology appropriate to the audience
- use digital resources to extend own knowledge and skills relevant to their role
- risk assess the organisational impact of decisions that they take
- use digital systems to identify productivity and performance improvements
- use digital technologies to operate effectively as part of a team, and with other stakeholders, enabling sharing of information and best practice
- maintain system security in line with organisational policies.
- support customers in the use of information, products and services through digital channels.
- diagnoses technical problems by identifying and applying tools and techniques to undertake fault finding, recording and rectification.
- maintain end-user systems physically or remotely. For example: software, hardware or operating systems
- provide and direct end-users to tools and resources to help them to resolve their digital problems.
Behaviours
- work independently and take responsibility to maintain productive and professional working environment with secure working practices.
- use own initiative when implementing digital technologies and finding solutions to stakeholder’s problems.
- professional approach to dealing with stakeholder’s problems.
- self-motivated for example: takes responsibility to complete the job.
- takes a sustainable mindset towards digital support activities ensuring climate change and the move to net carbon zero by 2050 is a consideration